Posted on: Monday April 8, 2019
Post by Karen Sereda, Collections Registration Associate (Natural History)
The incredible diversity of the Museum’s herbarium can only be credited to the dedicated collectors of botanical specimens, both modern and historical. Recently, while updating some herbarium specimens, I came across some plants in our collection dating from the early part of the 20th century. The importance of these specimens cannot be emphasized enough, as many of them come from locations that are no longer the same as when these collectors visited them. The stories of many of these early Manitoba collectors are fascinating.
John Macoun
John Macoun immigrated with his family to Canada from Ireland in 1850. Being unsatisfied with farming, John took up teaching in 1856 and developed an obsessive interest in botany. Although he had little formal education he became a Professor of Botany and Geology in Ontario in 1868, and in 1872 was recruited for railway surveys in the west. Due largely to his efforts, natural history came to be regarded as an important aspect of these surveys.
John published extensively, and his 1882 publication “Manitoba and the Great North-west” was wildly popular. It was as a botanical field naturalist, however, that Macoun’s abilities shone.
He was able to recognize new plant forms at first sight, and discovered many new species. Many of these were named after him using the specific epithet macounii.
John Macoun’s autobiography was published in 1922 by the Ottawa Field-Naturalists Club; it has now been digitized. Dr. Diana Bizecki Robson also highlighted John Macoun in one of her blogs.
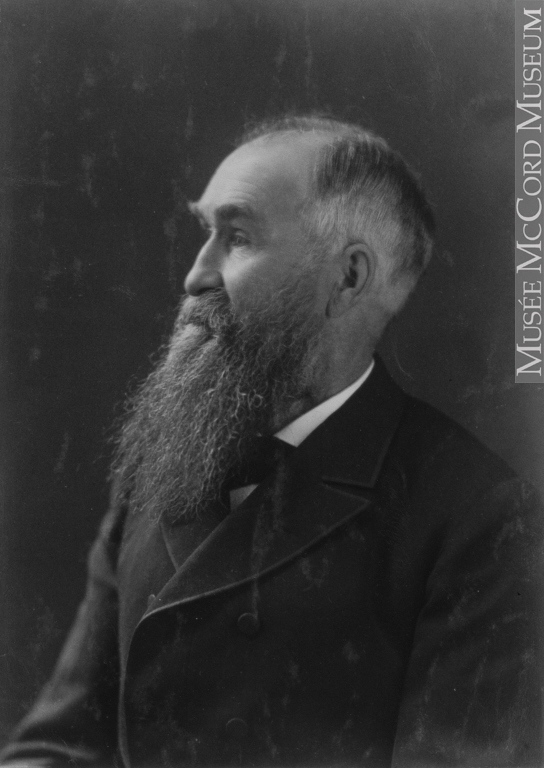

John Macoun in 1891. Image: McCord Museum
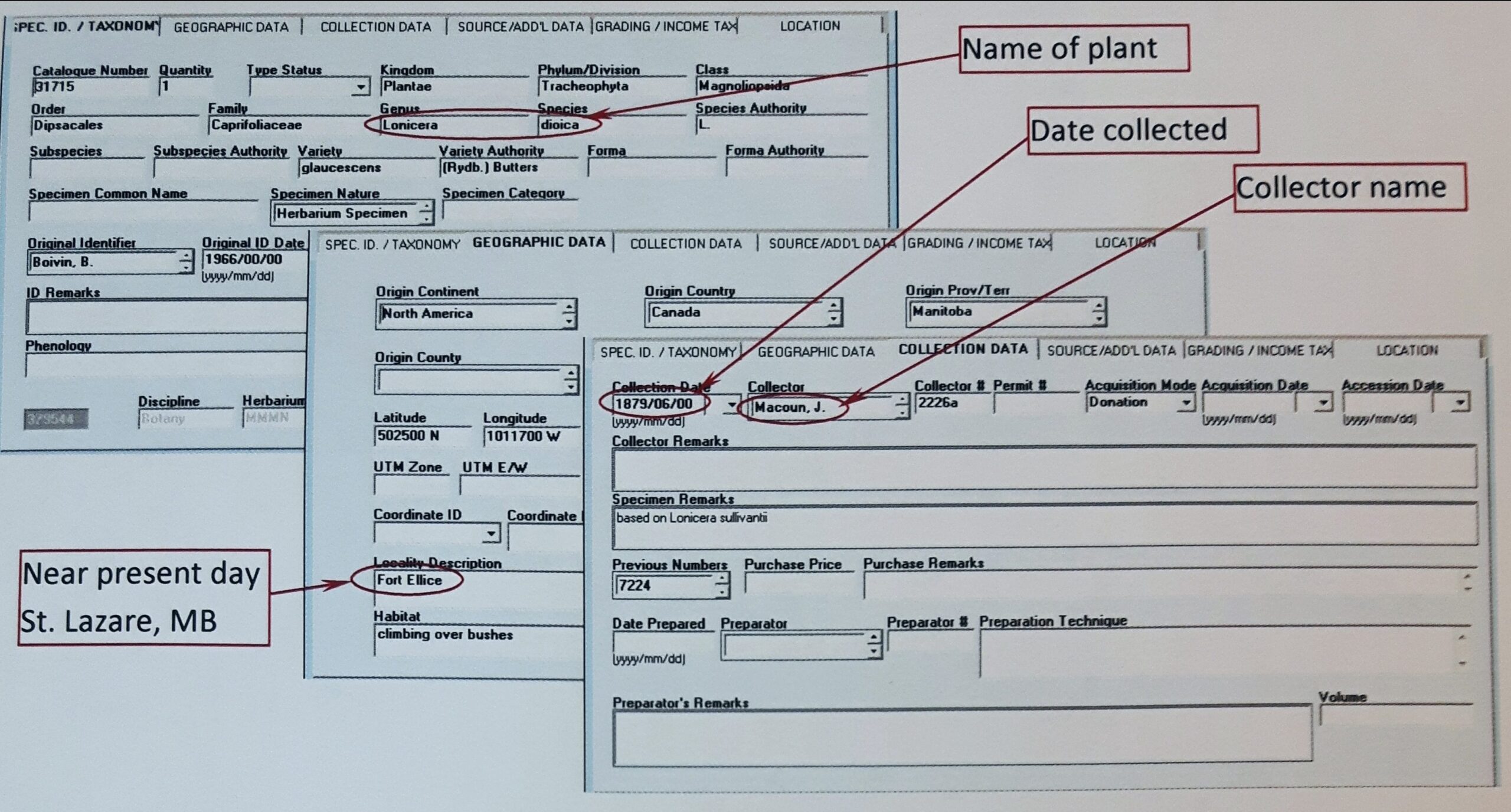
Screenshots of the catalogue entries of a botanical specimen (31715) collected by John Macoun in 1879 in Manitoba © Manitoba Museum.

Catalogued Ranunculus macounii (6348) specimen © Manitoba Museum.
William Alfred Burman
In 1875, William Alfred Burman was persuaded to immigrate to Canada at the age of 18. He studied theology and the natural sciences at university, and in 1880 was sent by the Anglican church to Griswold, now the Sioux Valley Dakota Nation, to teach and establish a mission.
While there, he became fluent in and wrote about the language of the Dakotas. As well, he helped to found the Forestry and Horticultural Association of Manitoba which still promotes horticulture on the prairies. Burman later returned to Winnipeg to lecture in botany and biblical literature, plus act as the steward and bursar for St. John’s College at the University of Manitoba. He had a high opinion of both John Macoun and Norman Criddle (to be discussed in Part 2), two amateur, yet extremely competent botanists. Burman was an avid nature lover, and was also an examiner in botany at the University of Manitoba for many years.
Reginald Buller
Reginald Buller was an eccentric man. Although he went by Reginald, his full name was actually Arthur Henry Reginald Buller.
He was hired by the University of Manitoba in 1904, and the Buller Building is named after him. One of the first six science professors, he taught botany and mycology, and was a prolific researcher.
A perpetual bachelor despite the interests of various women, he never owned a house in Winnipeg, but lived in various downtown hotels his 40 years in Manitoba. Buller was a serious billiards player, and also wrote poetry. He especially enjoyed writing limericks such as this one he based on Einstein’s theory of relativity.
There was a young lady named Bright,
Whose speed was far faster than light.
She set out one day,
In a relative way,
And returned home the previous night.
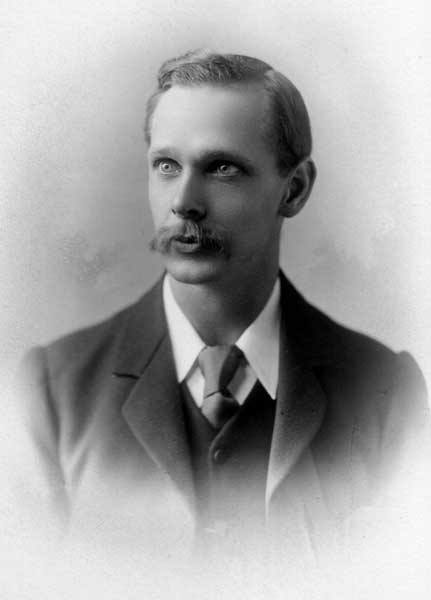

A.H. Reginald Buller in 1904.
Source.
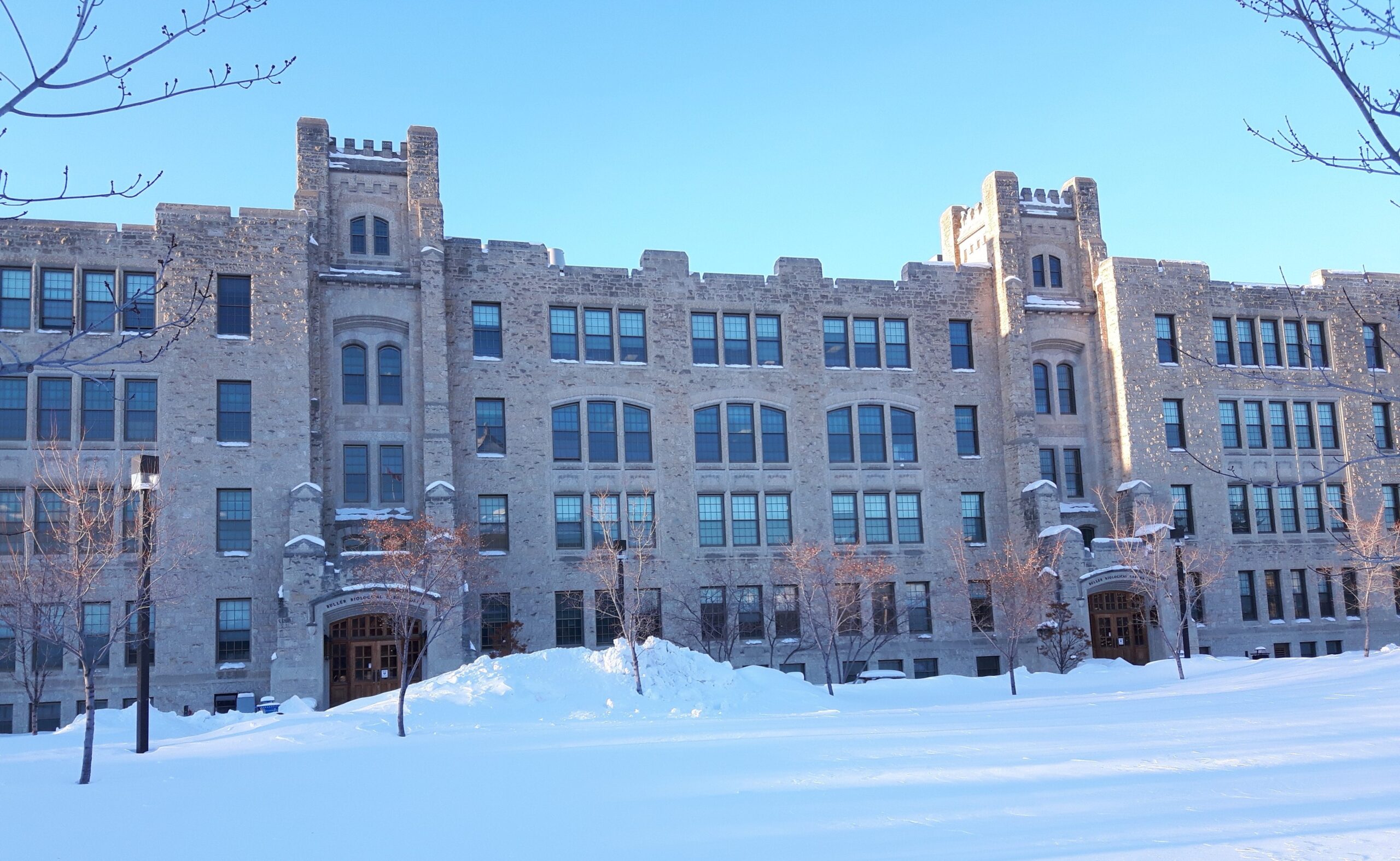

Today’s Buller Building at the University of Manitoba. © Manitoba Museum.
If you are interested in more information about Buller, you can read this article by Dr. Gordon Goldsborough.
Part 2 features the next generation of Manitoba botanists; Norman Criddle, Charles W. Lowe, and Margaret G. Dudley.