To celebrate Black History Month, Curator of History Roland Sawatzky joins forces with Naomi Dennie, a teacher in Seven Oaks School Division and creator of Amplify Us, a podcast series to amplify Black experiences in the Canadian educational system. They share the story you might not know about Winnipeg’s “Elks”.
Image above: Official greeting from Ernest C. Brown, the Exalted Ruler of Menelik Lodge No. 528, in the Souvenir Program of the 10th Anniversary of the Brotherhood of Sleeping Car Porters, 1952 (which replaced the Order of Sleeping Car Porters, established in 1917). Mr. Brown was himself a porter for the Canadian National Railway. H9-37-195, Manitoba Museum
Menelik Lodge No. 528 was founded by Winnipeg railway porters in 1917 to support the Black community with fundraising, education, and social activities. The Lodge was part of the North American fraternal society known as The Improved, Benevolent and Protective Order of the Elks of the World (IBPOEW). The IBPOEW was founded in Cincinnati in 1898 by Arthur James Riggs and Benjamin Franklin Howard, who wanted to form an alternative to the all-white Order of the Elks.
They began the society for “the expression of ideals, services and leadership in the black struggle for freedom and opportunity.” Lodge No. 528 also ensured financial support for members who became ill, and death benefits for relatives of deceased members. According to Sarah-Jane Mathieu, author of North of the Color Line: Migration and Black Resistance in Canada, porters also “likely used lodge meetings as covers for their union plotting.”

The “Elks,” as they were known, held regular meetings at 795 Main St., a building that still stands today beside the Sutherland Hotel. The Lodge had popular regalia, including purple fezzes and ribbons, and the usual oaths confirming mutual support. The Menelik Lodge held large annual picnics in August, as well as dances and banquets. Additionally, there was a Ladies Auxiliary and a “Junior Elks Herd” for kids.
The Elks were profoundly impactful to Winnipeg history and should be honoured for their commitment to the Black community and their involvement in political and social activism throughout their duration.
Fun Fact!
Menelik Lodge adopted its name from Emperor Menelik of Ethiopia, who was said to be the son of the Biblical figures Queen of Sheba and King Solomon. Emperor Menelik II (1844-1913) may also have been an inspiration, as he helped create the independent modern state of Ethiopia.
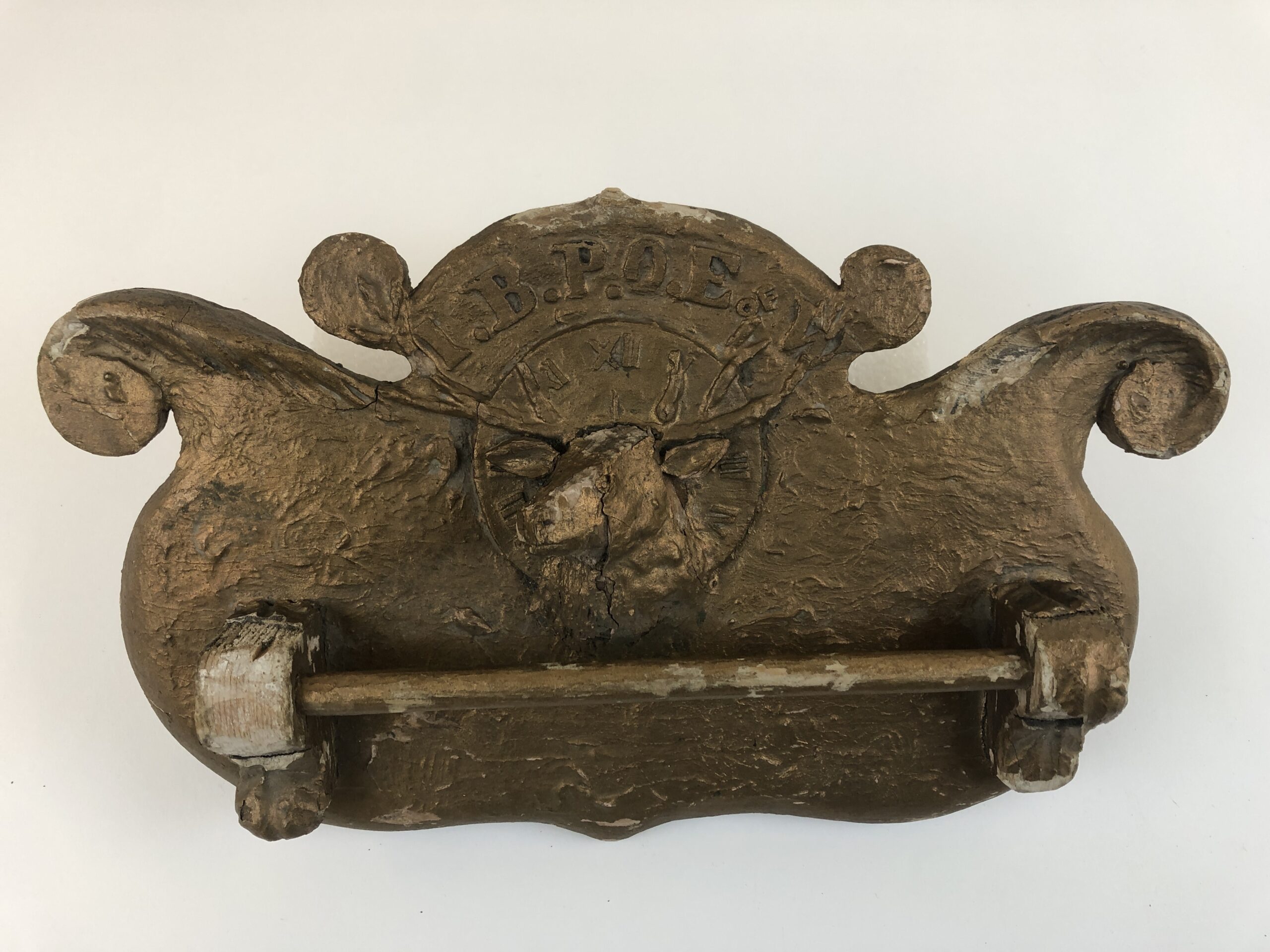

Join us in Museum Galleries Saturday afternoons in February to see these artifacts on display as part of our Black History Month pop-up mini-exhibit.
Bundle and save! Save 25% when you purchase tickets for all three attractions.